
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) have revolutionised the investment landscape, offering traders a versatile tool to access diverse markets. For traders, ETFs present an opportunity to implement sophisticated risk management strategies once reserved for institutional investors. This article explores how ETFs can be effectively used to manage risk in your trading portfolio.
ETFs are investment funds traded on stock exchanges, much like individual stocks. They typically track an index, sector, commodity, or other assets, but can be bought and sold throughout the day like ordinary stock. Unlike mutual funds, ETFs offer greater flexibility and often come with lower fees.
While ETFs can mitigate some risks through diversification, they are not without their own set of risks. Market risk affects all investments, and ETFs are no exception. Tracking error, where an ETF’s performance deviates from its underlying index, is another consideration. Liquidity risk can also be a factor, especially for narrowly focused ETFs.
Diversification is a cornerstone of risk management, and ETFs excel at providing instant diversification. By investing in a single ETF, you can gain exposure to hundreds or even thousands of individual securities. This spreads risk across multiple companies, sectors, or even countries.
For maximum diversification, consider broad-market ETFs like those tracking the S&P 500 or total stock market indices. These provide exposure to a wide range of companies across various sectors, reducing the impact of poor performance from any single stock or industry.
Proper asset allocation is crucial for managing risk. ETFs make it easy to build a balanced portfolio across different asset classes. For example, you might use a combination of stock ETFs for growth, bond ETFs for stability, and commodity ETFs for inflation protection.
A simple yet effective allocation for a moderate-risk investor might look like:
– 60% in a total stock market ETF
– 30% in a broad bond market ETF
– 10% in a diversified commodity ETF
This allocation provides a mix of growth potential and stability, which can be easily adjusted based on your risk tolerance and investment goals.
ETFs offer various hedging strategies to protect your portfolio during market downturns. Inverse ETFs, which move in the opposite direction of their underlying index, can be used to offset potential losses in your long positions. However, use these instruments cautiously, as they’re designed for short-term hedging and can be complex.
For example, consider an investor who holds $10,000 in an S&P 500 index ETF. If they’re concerned about a potential market downturn, they might hedge their position by investing $2,000 in an inverse S&P 500 ETF. If the S&P 500 falls by 5%, their main position would lose $500, but the inverse ETF would gain about $100 (5% of $2,000), reducing the overall loss to $400. This strategy can provide some protection against short-term market volatility.
It’s important to note that leveraged and inverse ETFs can be particularly risky and are generally not suitable for long-term, buy-and-hold investors. Always thoroughly understand these products before incorporating them into your strategy.
Overexposure to specific sectors can increase portfolio risk. Sector ETFs allow you to balance your exposure or hedge against sector-specific risks. For instance, if you’re heavily invested in technology stocks, you might consider reducing risk by investing in a healthcare or utilities sector ETF.
Some traders use a sector rotation strategy, shifting investments between different sector ETFs based on the economic cycle. While this can be effective, it requires careful analysis and timely execution.
Expanding your portfolio internationally can reduce country-specific risks and potentially enhance returns. ETFs make it easy to invest in foreign markets without the complexities of directly owning foreign stocks.
This approach provides exposure to various international markets, potentially reducing risk through geographical diversification. In 2017, when the S&P 500 returned about 21.8%, the MSCI Emerging Markets Index returned 37.3%, demonstrating how international exposure can sometimes outperform domestic markets.
You can use country-specific ETFs to target particular markets or opt for regional ETFs for broader exposure. When investing internationally, be aware of currency risks. Some ETFs hedge currency exposure, while others don’t, affecting your returns as exchange rates fluctuate.
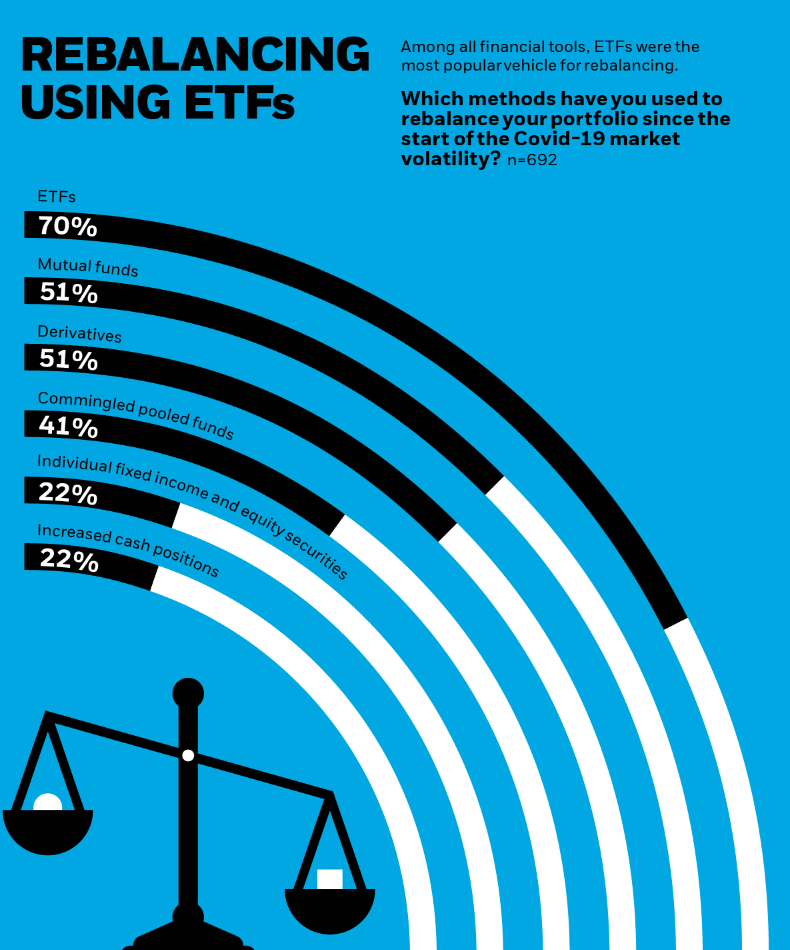
Regular rebalancing is essential to maintain your target asset allocation and manage risk. As different assets perform differently over time, your portfolio can drift from its original allocation, potentially increasing risk.
With ETFs, rebalancing is straightforward. Simply sell ETFs that have become overweighted in your portfolio and buy those that have become underweighted. The frequency of rebalancing depends on your strategy, but many investors rebalance annually or when their allocation drifts beyond predetermined thresholds.
To effectively manage risk with ETFs:
1. Research thoroughly: Look at an ETF’s expense ratio, tracking error, and liquidity before investing.
2. Use stop-loss orders: These can limit potential losses by automatically selling if an ETF’s price falls below a specified level.
3. Monitor and adjust: Regularly review your portfolio and adjust your strategy as needed.
4. Stay informed: Keep up with market trends and economic news that might affect your ETF investments.
Remember, while ETFs can be powerful risk management tools, they don’t eliminate risk entirely. Always invest within your risk tolerance and consider consulting with a financial adviser for personalised advice.
For those looking to implement these strategies, platforms like VT Markets offer the ability to trade a wide range of ETFs, providing access to diverse markets and risk management tools.
ETFs offer non-professional traders a range of tools for managing risk. From providing easy diversification to enabling sophisticated hedging strategies, ETFs can help you build a resilient portfolio. By understanding how to effectively use ETFs for risk management, you can navigate market uncertainties with greater confidence. As you apply these strategies, remember that successful investing is a journey of continuous learning and adaptation.