The coffee industry, valued at over 100 billion US dollars annually, boasts a thriving global market and is regarded as one of the most highly traded and consumed soft commodities worldwide. Coffee trading presents lucrative opportunities for traders, as it can be influenced by various external factors, including the prices of other commodities.
In this article, we will explore the process of trading coffee, delve into its historical significance as a soft commodity, and analyse the factors that impact its price, while also discussing the available trading options.

Coffee, classified as a soft commodity, is an agricultural product that shares similarities with other crops. Unlike hard commodities, which are extracted or mined, coffee is grown naturally.
It has been an essential part of diets across the globe for centuries. Originating in the Middle East, coffee gained popularity as a beverage in the 15th century.
European merchants discovered the flavourful bean in the 17th century, leading to the emergence of coffee trading. Merchants often gathered in coffee houses, which served as meeting places for trade discussions.
Over time, coffee plantations established by European colonists transformed into modern coffee suppliers. Today, the industry produces approximately 170 million bags of coffee beans each year, offering significant potential for traders.
The global coffee trade primarily revolves around two main types of coffee: Arabica and Robusta. These varieties possess unique flavours and are influenced by external factors that impact their respective prices. To determine which type of coffee to trade, it is crucial to comprehend the factors that affect the price of each variety.

Robusta accounts for around 30% of the coffee trading market and often trades at higher prices due to its demand among multinational corporations like Nestlé, which utilise the beans in global product lines such as Nescafé instant coffee. Vietnam is the primary producer of Robusta beans.
The specific geographic conditions necessary for coffee cultivation define the “coffee belt.” This belt extends from the equator to the Tropic of Cancer in the north and the Tropic of Capricorn in the south.
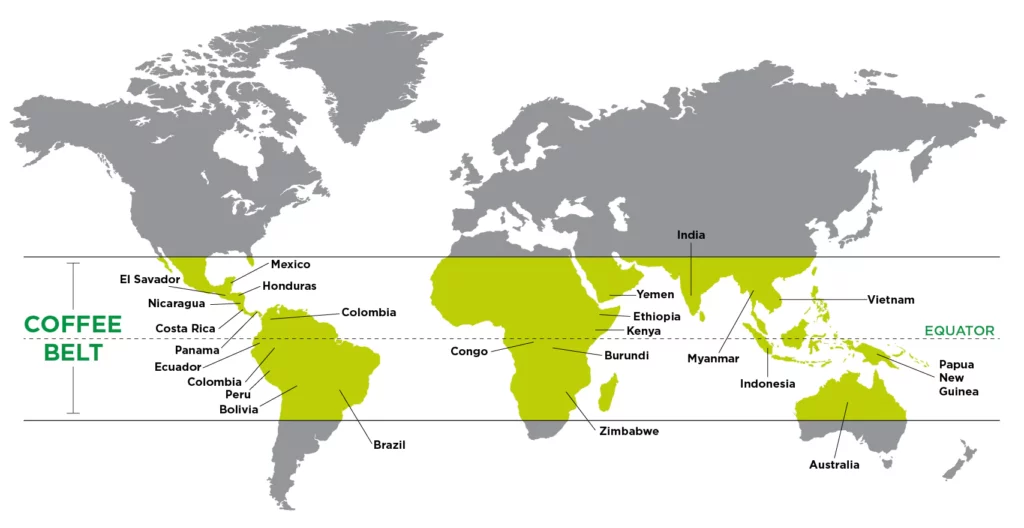
Although coffee of various types can be grown at different altitudes, the major coffee-producing nations include Brazil, Vietnam, Colombia, Indonesia, and Ethiopia.
Coffee trading occurs worldwide, with the largest importers of beans being the European Union, the United States, Japan, Russia, and Canada.
Given the multifaceted process of growing, harvesting, roasting, and transporting coffee, the coffee trade is subject to speculation and influenced by numerous factors that affect its price. Gaining familiarity with these fundamental aspects of the market is essential to master coffee trading.
The intricate nature of coffee production, which involves planting, growth, and harvesting, means that multiple factors must align for coffee to reach the market successfully and be traded.
Unexpected triggers can swiftly disrupt the coffee trading market, resulting in volatility. While volatility offers short-term profit opportunities for traders, those seeking stability may prefer to engage in coffee trading with a more consistent price index, utilising trends as guidance.
For those interested in coffee trading, selecting a preferred trading method is the first step.
VT Markets provides a user-friendly trading environment, simplifying the process of starting your coffee trading journey.
You can initiate your coffee trading experience by signing up for a free demo account, allowing you to practice trading coffee CFDs and futures on a risk-free platform for 90 days.
Alternatively, you can create a live trading account to jump straight into the action.
If you need guidance on opening your coffee trading account or wish to establish your trading portfolio, feel free to contact us. We are here to assist you in embarking on your trading endeavours.