Imagine you have $1,000 and want to invest in the foreign exchange market, commonly known as Forex. Traditionally, your $1,000 would only allow you to control a small trade size. However, with margin trading, you can now control a much larger position, say $100,000, with just a fraction of your own money. This means that even small fluctuations in currency prices can lead to substantial profits or losses. Welcome to the world of Margin Forex Trading!

Margin trading in the Forex market refers to the practice of borrowing funds from your broker to trade larger positions than what your account balance would typically allow. It is important to understand that while margin trading offers the potential for higher returns, it also increases the risk of significant losses.
In cash trading, you only use the money you have in your account to execute trades. In contrast, margin trading allows you to leverage your positions by using borrowed money from your broker.
One of the key concepts in margin trading is leverage. Leverage is the ratio between the amount of capital you have and the amount you can control.
For instance, if your broker offers a leverage of 1:100, you can control a position worth $100 for every $1 of your own money. Leverage can amplify both gains and losses, making it a powerful tool that requires careful use.
Margin, in the context of Forex trading, refers to the collateral you need to provide to open and maintain a leveraged position. It acts as a security deposit to ensure you can cover potential losses. The margin requirement is usually expressed as a percentage and varies depending on the broker and the currency pair you’re trading.
For example, with a 2% margin requirement, to control a $100,000 position, you would need to have $2,000 in your account. This means you are leveraging your account 50 times (100,000 / 2,000) to control that position.
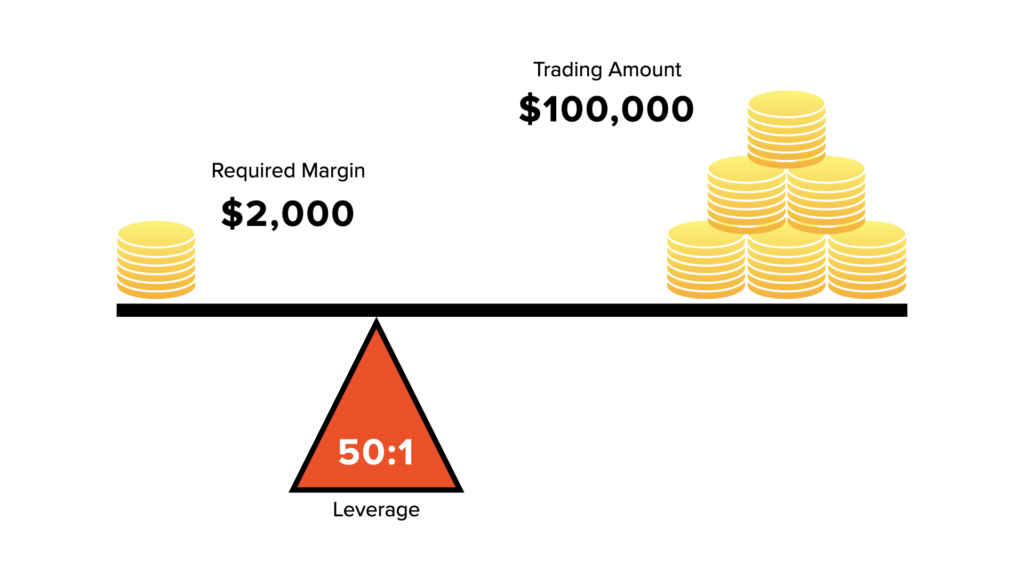
Leverage and margin are closely related. As mentioned earlier, leverage determines how much you can control relative to your account balance. The higher the leverage, the smaller the margin required to control larger positions.
However, traders need to be aware that while leverage can lead to significant profits, it also exposes them to more substantial losses. For instance, a 1% price movement in the opposite direction of your trade can lead to a 100% loss of the margin invested.
Let’s delve into how margin is used in Forex trading. When you open a leveraged position, your broker sets aside the required margin from your account balance as collateral. As long as your trade is active, the margin remains tied up. Once you close the trade, the margin is released back to your account, along with any profits or losses.
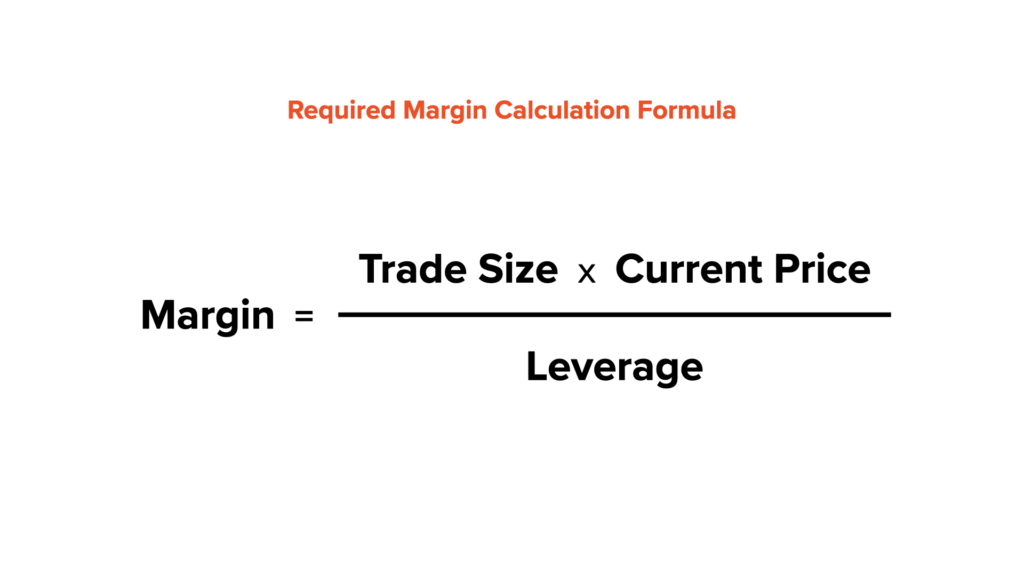
To calculate the required margin for a specific trade size, you can use the following formula:
Margin = (Trade Size * Current Price) / Leverage
To ensure you fully understand the margin requirements and leverage, let’s calculate them with a real-world example. Suppose you want to control a position of $50,000 on the EUR/USD currency pair with a leverage of 1:50.
Margin = ($50,000 * 1) / 50 = $1,000
Margin Calls and Stop-Outs: Protecting Your Investments
In the exciting world of margin Forex trading, understanding margin calls and stop-outs is essential to safeguarding your investments and ensuring responsible trading practices. These mechanisms act as safety nets provided by brokers to protect traders from potential devastating losses.
Margin Calls: Your Financial Alarm Bell
A margin call is a crucial warning signal that occurs when the equity in your trading account falls below the required margin level. In simpler terms, it means that your account balance is no longer sufficient to support the open leveraged positions you have taken.
Suppose you have a margin trading account with $5,000 and decide to open a leveraged position on the GBP/USD currency pair. The broker offers a leverage of 1:100, meaning you can control $100 for every $1 of your own money. You use your $5,000 to control a position worth $500,000 ($5,000 * 100), relying on the 1:100 leverage.
Now, imagine that the market moves against your position, causing a loss of $4,800. As a result, your account equity drops to $200 ($5,000 – $4,800), which is now significantly below the required margin to maintain your open position.
At this point, the broker will issue a margin call, notifying you that you need to add more funds to your account to meet the required margin level. If you fail to top up your account, the broker may automatically close your positions to prevent further losses.
Stop-Outs: Last Line of Defence
A stop-out is the next stage if a margin call goes unheeded. When your account equity falls further and reaches the stop-out level, the broker will automatically liquidate your positions to protect your account from going into negative territory.
To continue with our previous example, let’s assume that despite the margin call, you didn’t deposit additional funds to meet the required margin level. The market continues to move against your position, and the losses worsen. As your account equity drops below the stop-out level, your broker will intervene and close your position automatically to prevent your account from incurring more losses.
In our example, let’s say the stop-out level is set at 20% of the required margin, which would be $1,000 (20% of $5,000). When your account equity falls to $150 (3% of $5,000), which is below the stop-out level, the broker will execute the stop-out and close your position.
Understanding the significance of margin calls and stop-outs is vital in maintaining your financial well-being while engaging in margin Forex trading. It is crucial to be vigilant about monitoring your account’s equity and ensuring that you have sufficient funds to support your open positions, especially during periods of high market volatility.
Opening a Margin Trading Account
If you’re interested in margin trading, you’ll need to open an account with a reputable Forex broker that offers leverage. For example, you can open a margin trading account with VT Markets, a trusted broker known for its user-friendly platform and up to 500:1 leverage option.
When opening a live trading account, you’ll typically need to deposit an initial amount of funds, which will serve as your trading capital.
Margin Forex trading offers exciting opportunities and potential rewards, but it also comes with inherent risks that traders should be aware of. Let’s examine the pros and cons of engaging in margin trading:
Pros:
Cons:

Margin trading can be enticing for beginners, but it’s essential to approach it with caution and a solid understanding of the risks involved. Here are some valuable tips to help newcomers navigate the world of margin Forex trading safely and responsibly:
In conclusion, margin Forex trading offers the potential for substantial profits, but it also carries significant risks. Aspiring traders should approach margin trading with caution and always prioritise continuous learning and risk management. By understanding the concepts of margin, leverage, and risk, you can navigate the Forex market with greater confidence and success.