
On 7 March 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that the unemployment rate held steady at 3.9% in February, with 275,000 jobs added to the economy. As this news broke, the S&P 500 index jumped by 0.8% in early trading.
If you’ve ever wondered why stock markets react to employment figures, you’re not alone. The unemployment rate is a crucial economic indicator that can significantly impact financial markets. In this article, we will explore how unemployment rates influence various market sectors and asset classes, and what it means traders like you.
Before diving into its effects on the market, let’s clarify what the unemployment rate actually is. Simply put, it’s the percentage of the labour force that is jobless and actively seeking employment.
In the United States, the Bureau of Labor Statistics calculates this rate monthly, considering various factors to provide an accurate snapshot of the job market. In the UK, the Office for National Statistics performs a similar function.
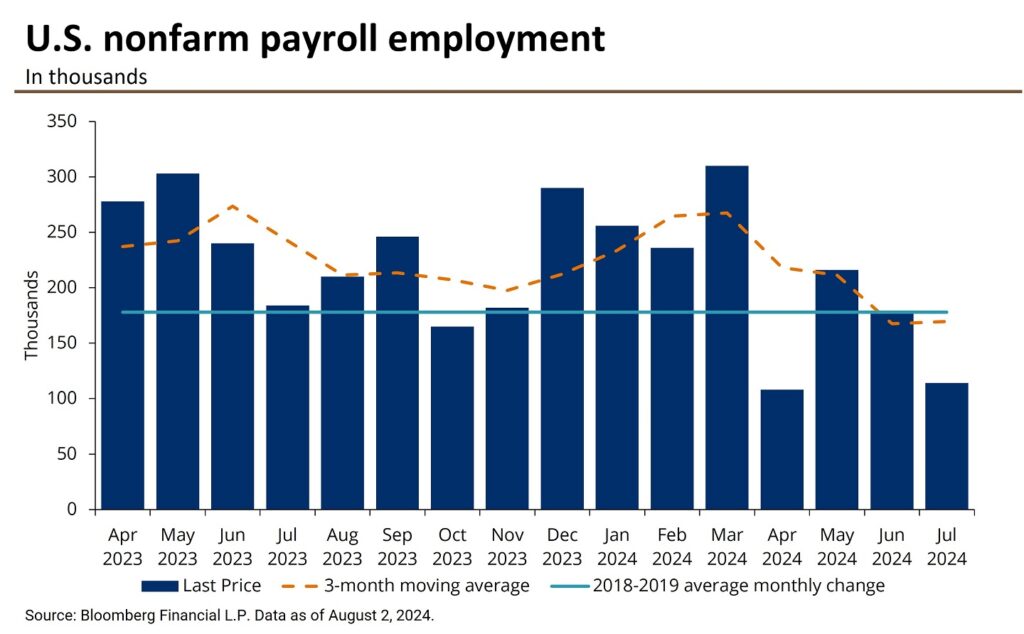
There are three main types of unemployment:
1. Frictional: Short-term unemployment as people transition between jobs
2. Structural: Long-term unemployment due to shifts in the economy
3. Cyclical: Unemployment caused by economic downturns
The unemployment rate is a key economic indicator because it reflects the overall health of the economy. Low unemployment generally signals a strong economy, while high unemployment often indicates economic struggles.
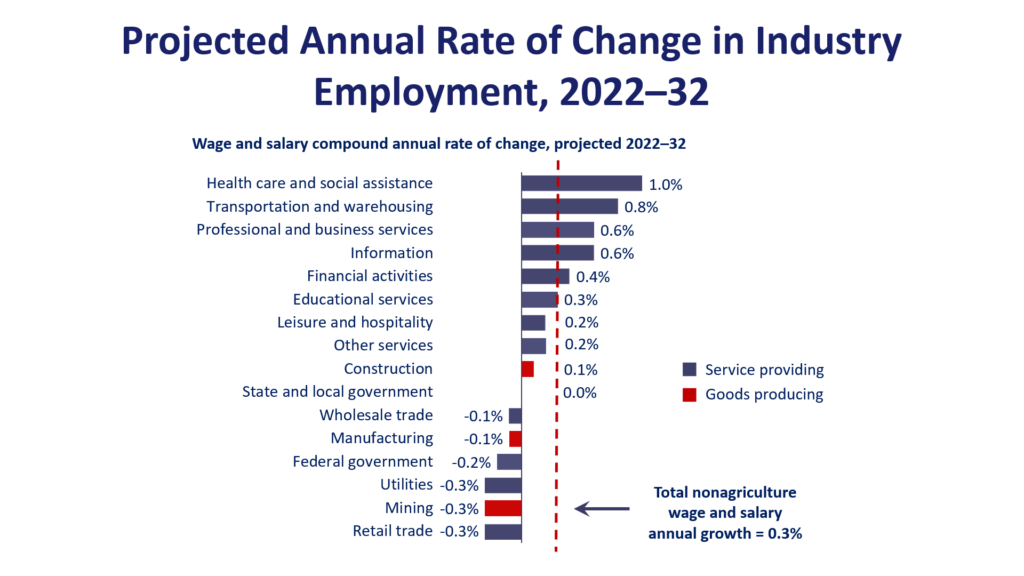
Different market sectors react uniquely to changes in unemployment rates. Let’s break down how some major sectors are affected:
Consumer discretionary
This sector, which includes retail, entertainment, and luxury goods, is highly sensitive to unemployment. When unemployment is low, people have more disposable income, boosting these companies’ performance. Conversely, high unemployment often leads to reduced consumer spending, negatively impacting this sector.
Financial
Banks and financial institutions tend to perform better when unemployment is low. With more people employed, there’s increased demand for loans and financial services. High unemployment can lead to loan defaults and reduced financial activity.
Technology
The tech sector’s response to unemployment can be mixed. While high unemployment may reduce consumer spending on tech products, it can also drive innovation as companies seek efficiency through technology.
Industrial
This sector, which includes manufacturing and construction, is closely tied to employment rates. Low unemployment often signals increased production and construction activity, benefiting industrial companies.
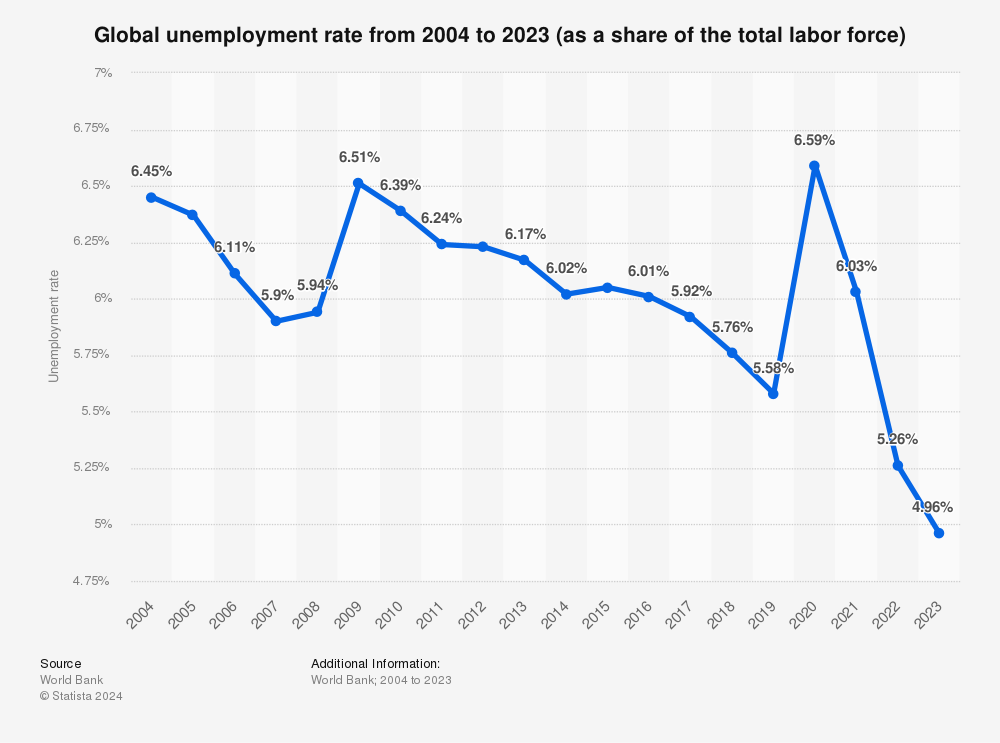
Unemployment rates don’t just affect individual sectors; they also influence various asset classes:
Stocks
Generally, low unemployment is positive for the stock market. It suggests a healthy economy with strong consumer spending and corporate profits. However, extremely low unemployment can lead to concerns about inflation and potential interest rate hikes, which may negatively impact stocks.
Bonds
The relationship between unemployment and bonds is complex. High unemployment often leads to lower interest rates, which can increase bond prices. Conversely, low unemployment might lead to higher interest rates, potentially decreasing bond values.
Commodities
Unemployment rates can indirectly affect commodities. Low unemployment usually indicates a strong economy, which can increase demand for commodities like oil and copper. However, this relationship can vary depending on the specific commodity and other economic factors.
Currencies
A country’s unemployment rate can influence its currency value. Low unemployment often strengthens a currency, as it suggests a robust economy. High unemployment may weaken a currency, as it could lead to lower interest rates and reduced foreign investment.
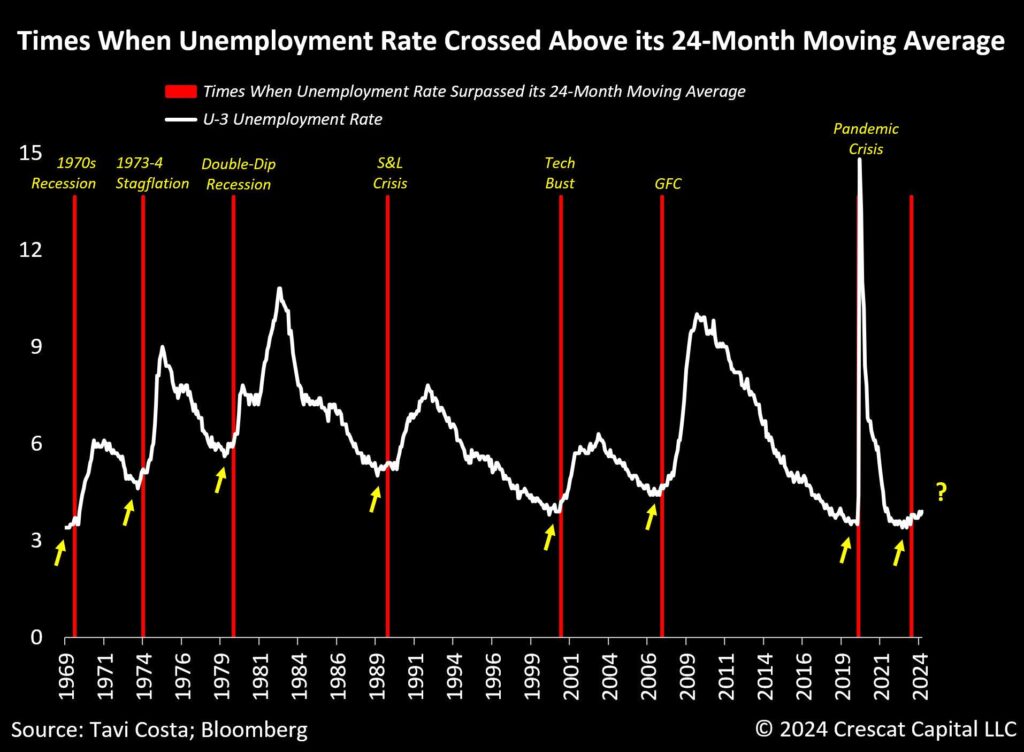
For traders, understanding how to use unemployment data can be a valuable tool:
1. Timing market entries and exits: Major unemployment reports can cause market volatility. Traders might consider waiting for the market to digest this information before making significant moves.
2. Sector rotation strategies: As different sectors respond differently to unemployment changes; traders might rotate their investments accordingly. For example, shifting towards consumer discretionary stocks when unemployment is falling.
3. Risk management: High unemployment periods might warrant a more conservative approach, while low unemployment could allow for slightly more risk tolerance.
4. Long-term vs. short-term approaches: Short-term traders might focus on the immediate market reactions to unemployment data, while long-term investors should consider the broader economic trends indicated by unemployment rates.

Stay informed by keeping an eye on these crucial reports:
1. Monthly US Jobs Report (Non-Farm Payrolls): Released on the first Friday of each month, this comprehensive report provides the headline unemployment rate and other important employment data.
2. Weekly Initial Jobless Claims: This report, released every Thursday, shows the number of new unemployment insurance claims filed by individuals seeking unemployment benefits.
3. Regional and industry-specific reports: These can provide more detailed insights into employment trends in particular areas or sectors.

To make the most of unemployment data in your trading strategy:
1. Don’t overreact to single reports. Look for trends over time.
2. Consider unemployment data alongside other economic indicators for a more complete picture.
3. Be aware of market expectations. Sometimes, the market reacts more to whether the unemployment rate met, exceeded, or fell short of expectations rather than the actual number.
4. Use reputable sources for unemployment data and analysis.
5. Remember that while unemployment is important, it’s just one piece of the economic puzzle.
Understanding how unemployment rates affect markets is crucial for all traders. By grasping these concepts, you can make more informed investment decisions and navigate market complexities with confidence.
Ready to put this knowledge into action? Consider trading with VT Markets, where you can utilise expert tools and analysis to capitalise on economic indicators like unemployment rates. Remember, successful trading isn’t just about numbers—it’s about understanding the economic story they tell. Start your informed trading journey with VT Markets today.